Multimodal, super-sensitive luminescent manometer based on giant pressure-induced spectral shift of Cr3+ in the NIR range
Title: Multimodal, super-sensitive luminescent manometer based on giant pressure-induced spectral shift of Cr3+ in the NIR range
Authors: M. Szymczak, M. Runowski, M.G. Brik, L. Marciniak
Journal: Chemical Engineering Journal
DOI: 10.1016/j.cej.2023.143130
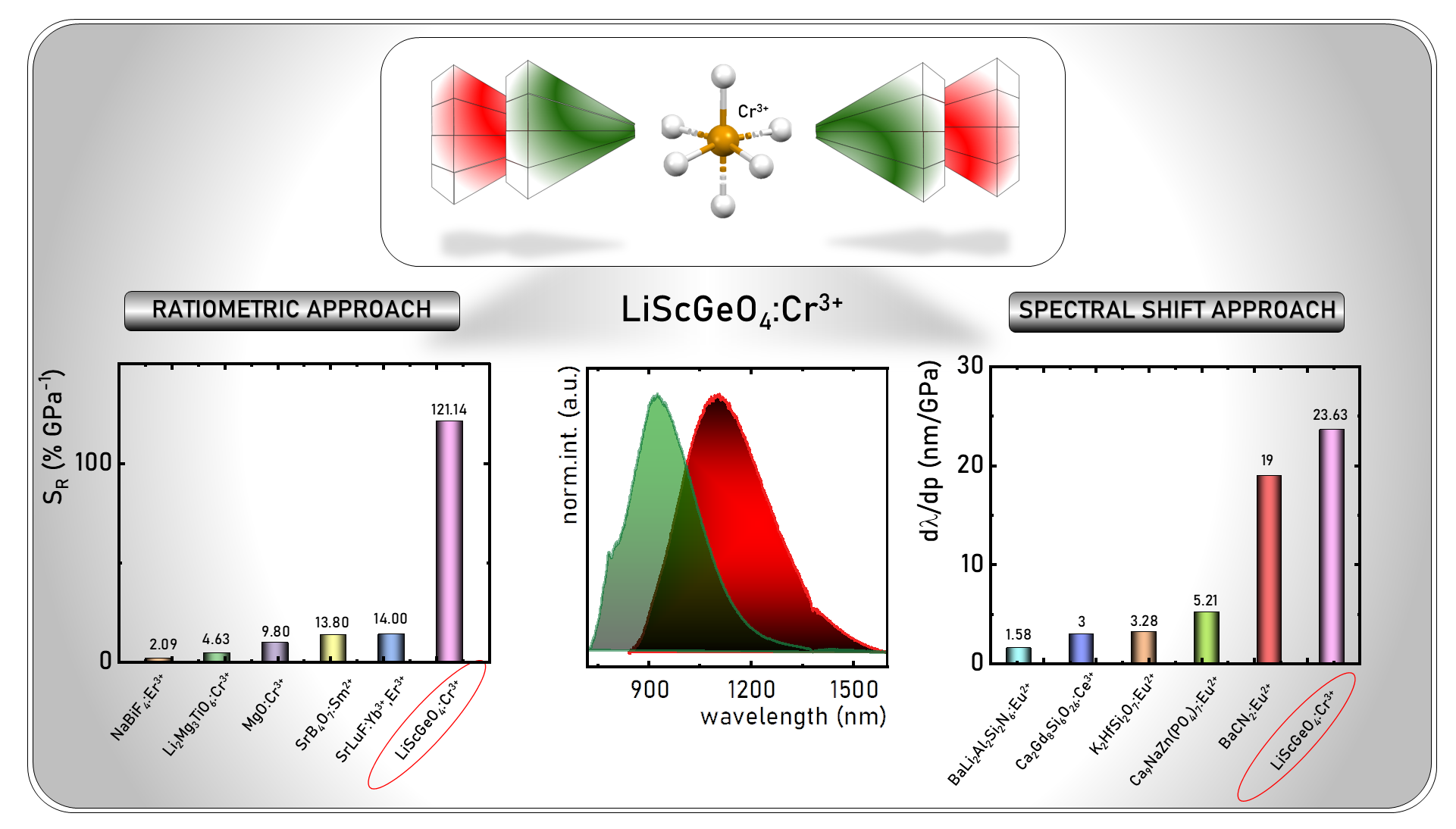
In their work, Prof. Marciniak's group described a luminescent manometer they had developed with record sensitivity to pressure changes.
Using the approach proposed by our group in luminescence manometry based on the ratiometric representation of the spectral shift of the Cr3+ ion band under applied pressure, it is necessary, in order to develop manometers with high relative sensitivity, to use a material in which the spectral shift of the emission band induced by pressure change is high. In response to these expectations, a manometer (LiScGeO4:Cr3+) was developed in which the 4T2→4A2 emission band exhibits the highest sensitivity to pressure changes of all manometers described to date of 23.63 nm/GPa. Hence, relative sensitivities of up to 120%/GPa were obtained in the ratiometric approach. As shown, the manometric properties of such a manometer (including operating pressure range and sensitivity values) can be altered by appropriate selection of the spectral ranges to be analyzed. This allowed to increase the functional versatility of the described material. What is particularly important is that the analyzed manometric parameter (luminescence intensities ratio) reveals relatively low sensitivity to temperature changes allowing reliable and temperature-independent pressure measurements.
The results described were obtained during the implementation of the NCN- 2020/37/B/ST5/00164 project.


